Saline water is water that is salty. This is the water that is found in the oceans and seas. The volume of salt in saline water can vary greatly. For example, the Dead Sea in Jordan is the saltiest sea in the world. There is so much salt that a person can float on top of the water without any effort. Sometimes lakes can contain saltwater (e.g. Great Salt Lake in Salt Lake City, Utah).
If groundwater has enough salt in it, then it is called saline groundwater.
Freshwater is found in rivers, lakes and even glaciers. Groundwater can be fresh, but the groundwater that is deeper than 150 metres runs the risk of being too saline to use as drinking water.
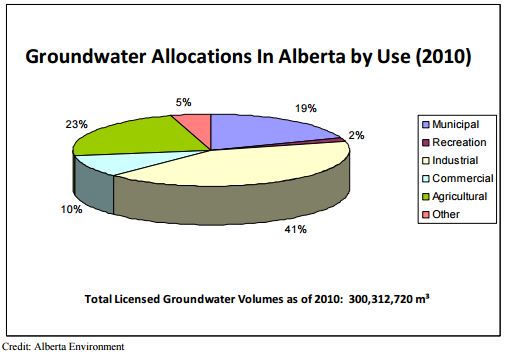
The Water Act regulates withdrawal, diversion and use of groundwater. If water is being used for anything other than household or traditional agricultural uses, a licence is required. Withdrawals must be approved for all industrial activities such as coal mines, coalbed methane development and gravel pits that may impact groundwater supplies, or any other project that could threaten groundwater resources. Additionally, the Environmental Protection and Enhancement Act regulates activity that affects groundwater quality. This includes the release of substances which can impact groundwater, the reclamation or remediation of contaminated groundwater sites, and the treatment of groundwater for drinking water supply [6].
We provide Canadian educational resources on water practices to promote conservation and sustainability. Our team crafts current and relevant content, while encouraging feedback and engagement.
The Canada WaterPortal is a registered charity, #807121876RR0001
We recognize and respect the sovereignty of the Indigenous Peoples and communities on whose land our work takes place.
© 2025 All Rights Reserved.