There are a variety of different terms for a raised structure that acts as a barrier between two areas. The terms berm, dike (or dyke), and levee are often used interchangeably to describe such structures that are used for flood mitigation. The main difference between the terms is how each is built to mitigate flooding. Both berm and levee refer to raised embankments that are either manmade or the result of excavated land. Note that “berm” can be used for a landscape feature not related to water management.
For our purposes, we will use berm to describe the raised banks intended for water management, as this is common language used to describe this form of flood mitigation.
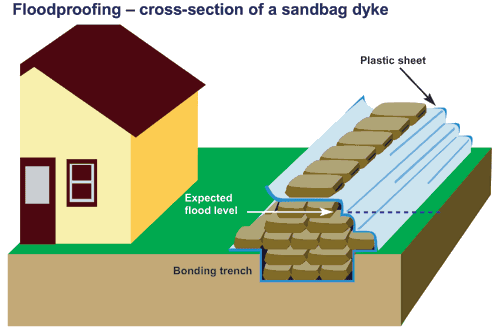
Berms contain dense sediment materials that decrease water velocity, control flow rates, and absorb excess water in the event of a flood. Normally placed in communities or sites prone to flooding, berms act as a barrier further mitigating the impacts of flood water. Berms are an effective form of flood mitigation, so long as they are built large enough to handle flood flows. For this reason, berms are often coupled with other mitigation measures, such as dams and dry ponds.
Typically, the primary concern for the lifetime expectancy of a berm is the river breaching or overtopping the berm. Therefore, these structures should be upgraded over time to accommodate higher river flows, to address settling, or if otherwise necessary. For example, Drumheller’s current project mentioned above came 30 years after initial construction.
The environmental impacts of berms include riverbank erosion, habitat destruction, and stream instability. These impacts are mainly caused by the increase in velocity that berms cause by limiting the room for water to flow.
Berms are built to contain flood waters and prevent riverbank breaches that could flood developments. Impacts on the surrounding watershed can be significant, due to high flow rates and subsequent erosion. The function of floodplains is also disrupted, because water is being confined to the stream, rather than allowing flow to expand across the floodplain.
Flood protection berms are intended to aid in flood situations by keeping high water out of certain areas. Therefore, they tend to be of little use in a drought.
We provide Canadian educational resources on water practices to promote conservation and sustainability. Our team crafts current and relevant content, while encouraging feedback and engagement.
The Canada WaterPortal is a registered charity, #807121876RR0001
We recognize and respect the sovereignty of the Indigenous Peoples and communities on whose land our work takes place.
© 2025 All Rights Reserved.